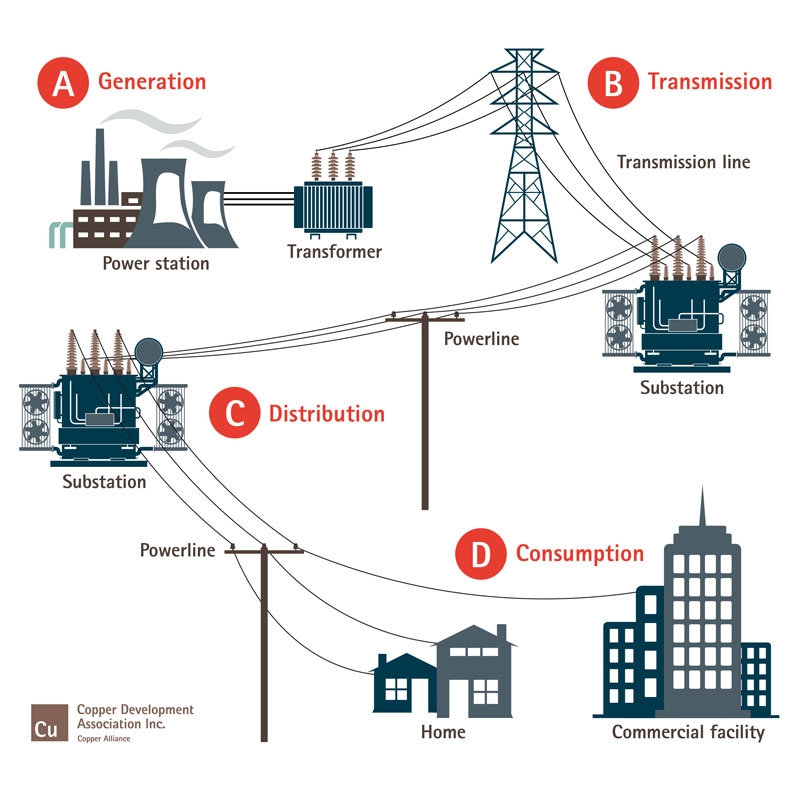
Copper is an integral part of grid infrastructure because of its reliability, efficiency and performance. Copper’s properties are vital to the interconnected network of plants, devices and lines that generate and distribute electricity and power throughout the country.
There are several key pieces of infrastructure that are built to support the delivery of electricity to consumers.
High Voltage Transmission
According to the Edison Electric Institute, the U.S. electric transmission network consists of more than 600,000 circuit miles of lines, 240,000 of which are considered high-voltage lines (230 Kilovolts and greater). These networks are designed to transport energy over long distances with minimal power losses. Copper is a key material component of transmission, which consists of structural frames, conductor lines, cables, transformers, circuit breakers, switches and substations.
Underground Transmission
- Longer life expectancy
- Reduced maintenance costs due to less exposure
- Protection from weather and other external hazards
- Advantages of copper cables
Microgrids
Microgrids are localized grids that can disconnect from the traditional grid and operate independently. Because of this, microgrids strengthen grid resiliency by helping to alleviate grid disturbances by allowing for faster system response and recovery. Microgrids also support a flexible and efficient electric grid by enabling the integration of distributed energy resources like solar and wind energy. The use of localized energy lowers energy losses in transmission and distribution, further increasing efficiency
Latest in Grid Infrastructure:
Education
- U.S. Needs Electric Vehicles; Our Grid Needs Help to Meet Demand
As electric vehicles (EVs) become more common across America, policymakers must prioritize our electric grid and ensure that it can handle the increasing demand. This op-ed from Zolaikha Strong, Director of Energy Policy and Electrical Markets, Copper Development Association, International Copper Association, highlights the progress and investments that have already been made in EVs by the federal and state governments, and encourages policymakers to further address grid modernization. - Protect the Grid, Secure the Nation
Protection of our nation’s energy grid today has never been more crucial as the FBI has stated that cyber-attacks are the primary threat facing the country. Couple that along with the new Clean Power Plan administered by the White House and US EPA with goals of reducing CO2, there is a major focus on the nation’s infrastructure. Copper continues to be a primary resource for building and protecting our nation’s grid due to its superior reliability, conductibility, and durability. - A secure energy grid starts with copper
It’s not hard to imagine the role that energy plays in our daily lives — in fact it becomes immediately apparent when we experience even a brief power outage in our home or workplace. Quite simply, it stops us in our tracks. - Video - Will electric transportation strain utility power generation?
Edison Electric Institute’s Kellen Schefter talks about vehicle electrification and its potential impact on the grid at CDA’s 2018 Electric Vehicle Summit. - Video - Will electric transportation strain utility distribution?
Edison Electric Institute’s Kellen Schefter addresses transportation electrification and if it will strain utility distributions at CDA’s 2018 EVs: Navigating the Road Ahead Summit CDA’s 2018 Electric Vehicle Summit. - Video - Will vehicle to grid transform how utilities manage energy use?
Darren Epps, from Southern Company, discusses if vehicle to grid will transform the way utilities manage energy use at 2018 Electric Vehicle Summit.
Case Studies
- Copper Connects Microgrids with Smart Grids: Copper Usage Is Key to Modern Electric Grids [PDF]
Microgrids are making the world more efficient and less reliant on huge, ineffective power systems.
