 Copper speciment in instron tensile tester with video extensometer.
Copper speciment in instron tensile tester with video extensometer. Photo Courtesy of Instron Corp.
The modulus of elasticity, also called Youngs Modulus, is the constant relating stress and strain for a linearly elastic material. In practical terms, modulus of elasticity is a measure of a materials stiffness. The higher the modulus of elasticity, the stiffer a material is. Modulus of elasticity is determined by chemical composition and is not significantly changed by cold working or heat treatment. Modulus of elasticity is expressed both in lb/in2 and MPa (MegaPascals). 1 MPa is equal to 1 Newton/mm2.
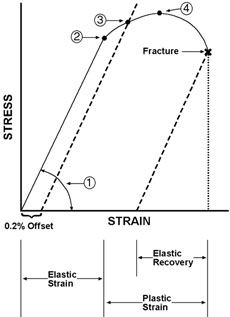 Figure to the left shows a typical stress-strain curve for a material and will be useful in describing some of the physical properties. (1) is the slope of the elastic portion of the stress-strain curve termed the modulus of elasticity. By definition, the proportional limit, (2) is the point within the elastic range where the stress-strain curve departs from being linear. This point can also be thought of as the elastic limit. Beyond this point, the specimen will show permanent deformation, after removal of the load, due to plastic strain.
Figure to the left shows a typical stress-strain curve for a material and will be useful in describing some of the physical properties. (1) is the slope of the elastic portion of the stress-strain curve termed the modulus of elasticity. By definition, the proportional limit, (2) is the point within the elastic range where the stress-strain curve departs from being linear. This point can also be thought of as the elastic limit. Beyond this point, the specimen will show permanent deformation, after removal of the load, due to plastic strain.
